Appendix A: Reconstruction of Minkowski Metric from Geometric Evolution Circle
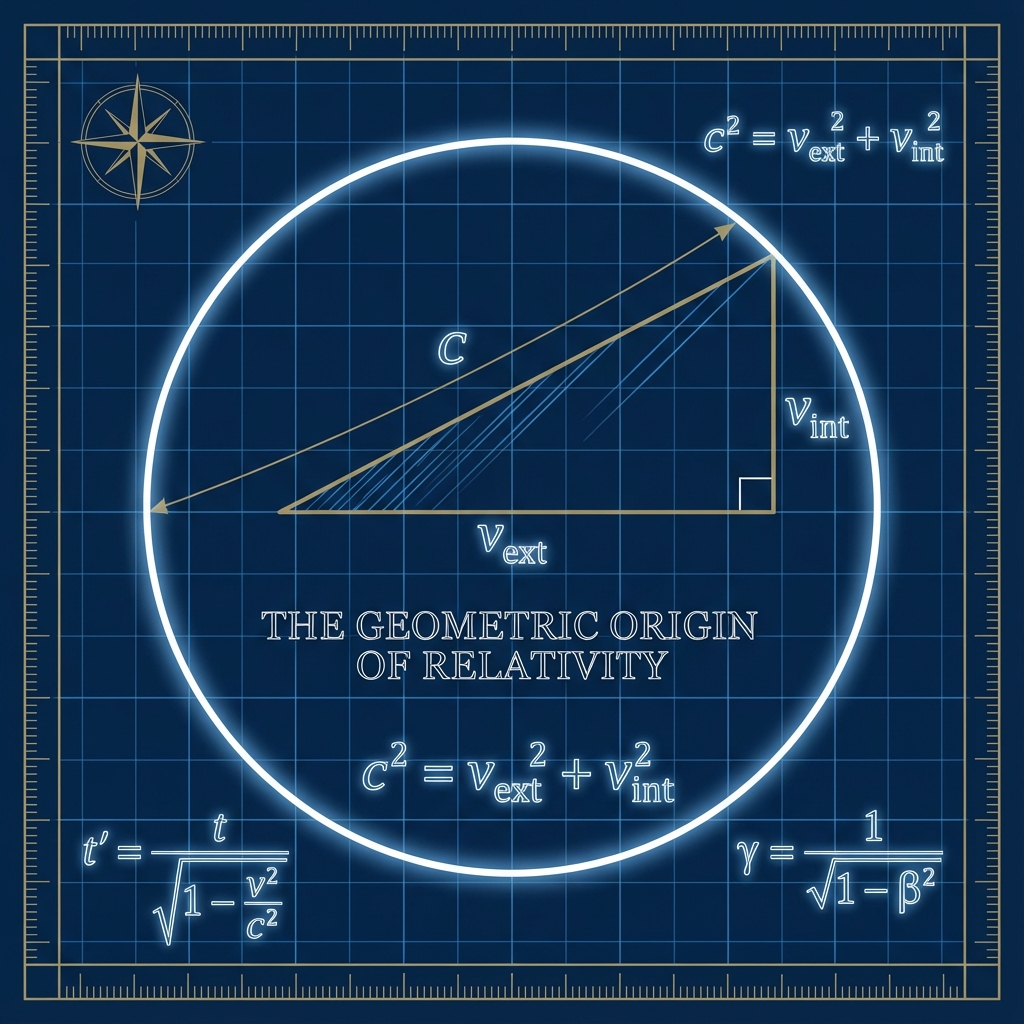
This appendix aims to prove that the core geometric structure of special relativity (Minkowski metric) can be strictly derived as a special case of the “sector Parseval identity” in Fubini-Study geometry.
1. Geometric Setup
Let the cosmic state be a normalized vector in Hilbert space. According to Axiom A1, its evolution rate is constant :
2. Orthogonal Decomposition
We introduce two orthogonal projection operators (external/spatial sector) and (internal/temporal sector). According to Parseval’s identity, the squared norm of the total evolution vector equals the sum of squared norms of its components:
where , . This is the mathematical form of the “Great Trade-off” in the main text.
3. The Identification
To establish connection with the physical world, we make the following natural mapping:
-
External velocity: Identify as the spatial coordinate velocity .
-
Internal velocity: Identify as the rate of proper time () flow. For dimensional consistency, we set .
4. Derivation of the Metric
Substituting the above definitions into formula (A.1):
Multiplying both sides by :
Rearranging, we obtain the expression for proper time :
Or written in line element form (using signature convention):
This is exactly the standard Minkowski Line Element. This shows that Lorentz symmetry is not an a priori geometric axiom, but a manifestation of isotropic evolution in Hilbert space under specific projections.